ABB FGF Robot Printers

Above: ABB 3D Printing PowerPac add-in to RobotStudio/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
3D Printing is a rapidly growing manufacturing technology of current times. According to ABB’s estimates, the overall market size of the 3D printing industry is set to double in the next 5 years with a CAG of 22% annually.
The drive to enter this market basically stems from the fact that this market is largely untouched by Robot manufacturers. And by entering the market at this point in time and by efficiently leveraging its existing technology and expertise ABB hopes to capture a significant chunk of the ripe market.
ABB ROBOTICS
ABB, the Swiss-Swedish multinational corporation, is one of the leading supplier of industrial robots and robot software, equipment and complete application solutions. It’s portfolio includes industrial robots, controllers, equipment and accessories, application software, RobotStudio, etc. The scope of its reach can be gauged from its impressive numbers like more than 400,000 robots installations worldwide with active facilities in more than 53 countries.
ABB ROBOTSTUDIO
ABB’s RobotStudio is an offline robot programming and realistic simulation software claimed to be the world’s most used offline programming tool for robotics. Its offline programming capability is its USP and ABB believes that it is the best way to maximize return on investment for robot systems. It allows for PC programming in office environment thus eliminating the need for shutting down production operations while programming.
RobotStudio provides the tools to increase the profitability of any robot system by letting the user perform tasks such as training, programming, and optimization without disturbing production.
The advantages of RobotStudio are as follows:
- Risk reduction
- Quicker start-up
- Shorter change-over
- Increased productivity
ABB ROBOTSTUDIO 3D PRINTING POWERPAC

Above: ABB RobotStudio 3D Printing PowerPac/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
Over the years, ABB has developed multiple PowerPacs (or add-ins) to its RobotStudio software. The recent one being for the 3D printing technology. The 3D Printing PowerPac is basically an Add-In that extends RobotStudio capabilities with 3D printing functionality. It will be used to perform numerous software tasks for its upcoming Robot 3D printer. The tasks like generating RAPID code from g-codes (geometric codes generated for traditional small 3D printers), print orientation, tool orientation, defining process parameters, other movement parameters and other similar necessary tasks.
The 3D Printing PowerPac will also run simulations for 3D printing to check for any inconsistencies, errors to suggest required corrective action.
ABB 3D PRINTING WORKFLOW
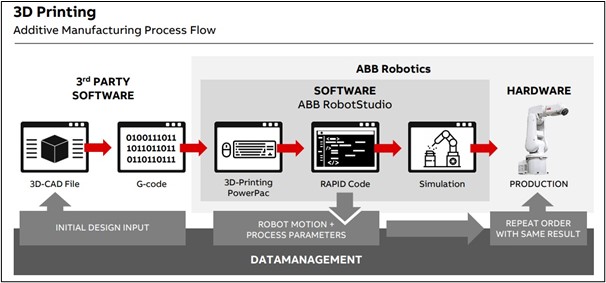
Above: ABB’s 3D Printing Workflow/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
The above workflow chart clearly defines the areas of intervention by the ABB Robotics. ABB Robotics will take over the 3D printing process from the generation of g-code files by traditional slicing software and then run them through its software to generate RAPID code and then move forward towards 3D printing the object in question.
CAD Stage to Final Modeling in 30 Minutes

Above: The 3D Printing PowerPac allows users to move from CAD stage to Final modeling in under 30 minutes/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
ABB has leveraged its decades-long expertise and experience in developing the latest add-in 3D Printing PowerPac to bring professional simulation and offline programming capabilities to the 3D printing technology. This state-of-the-art capability will enable users to rapidly move from the CAD stage to final modeling stage within 30 minutes. A huge advantage to manufacturers to produce an even faster output.
By combining the professional software, with ABBs high-performance robots with established standards, the users will be able to rapidly produce high-quality 3D printed objects for a variety of industrial applications more efficiently.
100% Simulation from Standard G-Code files
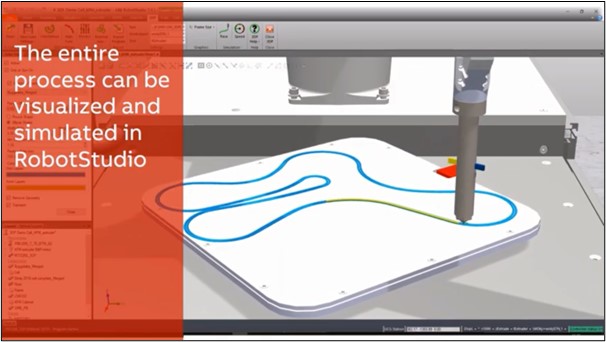
Above: 100% Simulation from Standard G-Code files/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
The core advantage of ABB’s 3D Printing PowerPac is that a standard G-code file is all that is needed by robots to start its 3D printing process. Traditional methods of 3D printing using machines are time-consuming as programming the printing paths involves plotting millions of points and trajectories.
ABB’s 3D Printing PowerPac can easily translate any standard g-code file into ABB’s simulation environment and robot code. This new piece of software allows ABB to generate robot commands from standard g-code files automatically. This allows manufactures to visualize and simulate the entire process in RobotStudio.
Integration of Multiple 3D Printing Technologies
ABB’s software suite is not limited by the type of 3D printing process. It supports a variety of additive manufacturing processes, such as welding, printing with granules or concrete, and is ideal for low-volume, high-mix printing. Typically, manufacturer’s 3D print prototypes before they begin mass production, architects print building components and models, and they can now print shapes that could not otherwise be produced.
3D PRINTING MATERIALS
With ABB’s 3D Printing PowerPac, there is no limitation on the type of 3D printing process and the material used. It can work with various materials.

Above: 3D Printing Materials/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
The add-in software can work with materials like plastic & composite, concrete & ceramics, metals like arc & laser welding and even food. In a last year project with UPM, the software helped in successful 3D printing of UPM Formi 3D – a 100% recyclable bio-composite material.
Benefits of 3D Printing PowerPac
Above: ABB enables 3D Printing via RobotStudio® for faster digital manufacturing/Courtesy: ABB Robotics
Converts G-code to RAPID code with support for multiple print processes
The PowerPac reads G-code files and converts them to RAPID code, supporting processes such as welding, dispensing, and granulate extrusion.
No manual RAPID programming needed
The complete RAPID print program is generated automatically; no additional RAPID programming is needed.
Interpolation of external axes
Tools available for calculating interpolation of linear and rotational coordinated external axes to provide smooth movement.
Granulate extrusion can be controlled as integrated robot axis
If the extruder screw is driven by an ABB compatible motor, it can be controlled as an integrated robot axis, which provides precise process control.
No limitation on the number of G-code coordinate points
Coordinate data is loaded dynamically during execution, which enables printing very large objects.
Filtering G-code points
Different tools to filter out unnecessary G-code points for smoother robot movement.
Reachability control
Tools to check the reachability of the whole printing area before the print starts.
Simulate printing in RobotStudio
Before the print program is transferred to the physical robot, it can be simulated and verified on RobotStudio.
NOTABLE APPLICATIONS OF ABB 3D PRINTING POWERPAC
ABB’s 3D Printing PowerPac has found many real-world applications. Some of them are quite famous but not many know that the software driving those projects was ABB’s 3D printing PowerPac. Let us explore these applications.
ABB + UPM + Prenta Large-Scale Robotic 3D Printing
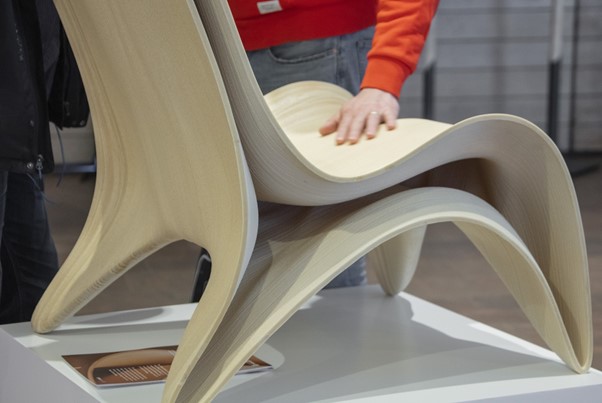

Above: ABB & UPM demonstrated large scale robotic 3D printing of wood composite applications, using granulate biocompatible cellulose material/ Courtesy: UPM-Kymmene Oyj
In 2019, UPM, a Finnish biopolymer specialist, collaborated with ABB & Prenta Oy, a Finnish technology industry company focused in 3D-printing, to demonstrate large-scale robotic 3D printing applications.
The collaboration efficiently enabled large granulate-based 3D printing. The material used was UPM Formi 3D – a 100% recyclable bio-composite material. The project was selectively chosen as the large-scale printing opens new possibilities for designers and manufacturers. The robot-based granulate printing clearly saved time and costs thereby achieving efficient fabrication of large-scale 3D printed parts. The potential areas of business include furniture design, molding and marine industry applications.
At the 2019 Nordic 3D Expo where the companies demonstrated a wood composite application, says Riku Rusanen, CEO of Prenta Finland said, “An industrial robot printing together with UPM Formi 3D biocomposite enables large components to be 3D printed with high geometrical tolerances. The PrentaRobo is designed for the manufacturing industry as a tool to create new and cost-efficient products”.
ABB + MX3D
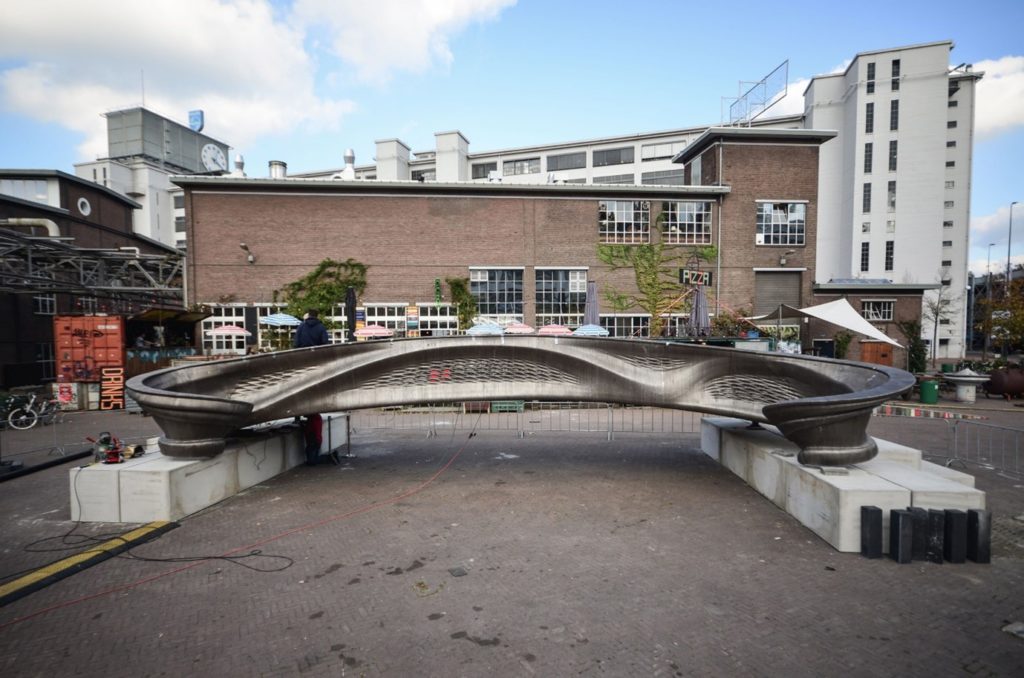

Above: MX3D unveiled a 3D Printed Steel Bridge in the Netherlands in 2018/Courtesy: MX3D
In the year 2018, MX3D, the Dutch robotics company, unveiled a 3D printed steel bridge measuring 12-meter in length and constructed using Robotic Additive Manufacturing (RAM) technology.
This technology basically used a Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) technology attached to ABB robotic arms. The bridge
ABB FGF Robot Printers
It seems like some information is already out there.
Anders Spaak is the engineer in Sweden who has been working on the integration between robot code and slicer. Basically, the part is sliced and after that run into RobotStudio (ABBs robot program) and the print can be started.
Extruder is currently from https://kfmmaskin.se/ – (A basic plastic extruder company, not specifically for 3D printing as I know of.
Printing with pellets, pictures in our folders on Drive





